Tag: Trump
Bi-Weekly Geopolitical Report – Investment Implications of the New US National Security Strategy (January 12, 2026)
by Patrick Fearon-Hernandez, CFA | PDF
As required by law, the new United States administration released its updated National Security Strategy in December 2025 (NSS 2025). As many observers have noted, the document marks a dramatic shift from the traditional NSS documents of the Cold War and the Globalization eras, not only in terms of threat assessments and priority initiatives, but also in terms of length, tone, and focus. In this report, we drill down to the investment implications of the new strategy if it is implemented as written. Our bottom-line assessment is that the new strategy could lead to significant changes in the global security environment, which in turn portends big potential changes in the global investment environment as well. The new strategy could mean significant shifts in global trade and investment flows, in the nature and origin of investment risks, in the policy responses that might be expected in a crisis, and among the most important policymakers worldwide.
Since we at Confluence have long tracked the evolving geopolitical landscape and identified many of the changes now incorporated in NSS 2025, we have been ahead of the game in adjusting our global strategies. Many of the investment implications we identify here are consistent with the ideas we have presented previously, such as a trend toward fracturing and disintegration among the nations of the world, less efficient trade and investment flows, and increased risk of conflict. In this report, we also offer several new ideas that complement these observations.
Don’t miss our accompanying podcasts, available on our website and most podcast platforms: Apple | Spotify
Bi-Weekly Geopolitical Podcast – #76 “China’s Rising Power and the Implications for US Hegemony” (Posted 10/27/25)
Bi-Weekly Geopolitical Report – China’s Rising Power and the Implications for US Hegemony (October 27, 2025)
by Patrick Fearon-Hernandez, CFA | PDF
In a recent report, we noted that the world is now transitioning away from its 30-year era of Globalization, when the United States mostly embraced its traditional role as global hegemon, i.e., the big, dominant country that provides international security, ensures relative order, and issues the reserve currency. Our previous report showed that the world is now entering a new era of Global Fracturing or, potentially, Chinese Hegemony. In this report, we take a deeper dive into the current US-China balance of power. We show that in all key aspects of power — military, diplomatic, technological, and economic — the balance appears to be shifting noticeably in favor of China. As this monumental shift in international relations becomes more obvious, US leaders and voters are increasingly struggling to decide whether they want to cede hegemony to the Chinese, defend it, or reform it into something that is more “America First.” Whatever they decide, the US role as global hegemon is changing as China’s relative strength increases. We conclude our report by discussing the investment implications of this change.
Don’t miss our accompanying podcasts, available on our website and most podcast platforms: Apple | Spotify
Bi-Weekly Geopolitical Podcast – #72 “Tariff Trilemma: The Three Rs Driving US Trade Policy” (Posted 9/2/25)
Bi-Weekly Geopolitical Report – Tariff Trilemma: The Three Rs Driving US Trade Policy (August 25, 2025)
by Thomas Wash | PDF
Not all tariffs are created equal. Throughout the history of the United States, tariffs have been employed to achieve three primary objectives: (1) to pressure other governments into lowering their own trade barriers, (2) to generate revenue, and (3) to protect domestic industries. While ideally these goals would be achieved simultaneously, trade policy often presents a “trilemma,” where pursuing two of these objectives comes at the expense of the third.
This report explores the distinct types of tariffs, their impact on financial markets, and what recent trade developments indicate for the future of the American economy. As always, we wrap up with the implications for investors.
Don’t miss our accompanying podcasts, available on our website and most podcast platforms: Apple | Spotify
Asset Allocation Bi-Weekly – #143 “The Hidden Battle in the ‘One Big, Beautiful Bill'” (Posted 6/30/25)
Asset Allocation Bi-Weekly – The Hidden Battle in the “One Big, Beautiful Bill” (June 30, 2025)
by Thomas Wash | PDF
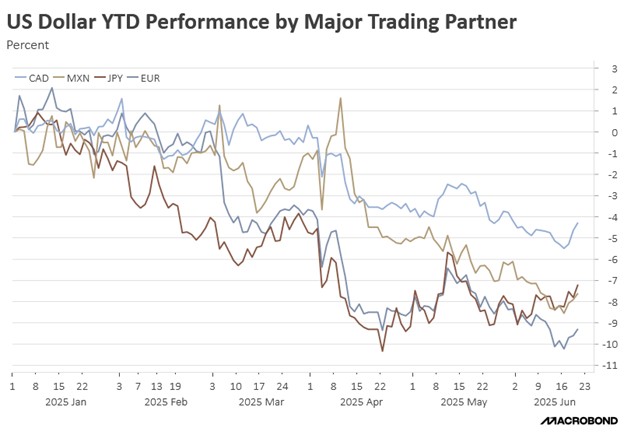
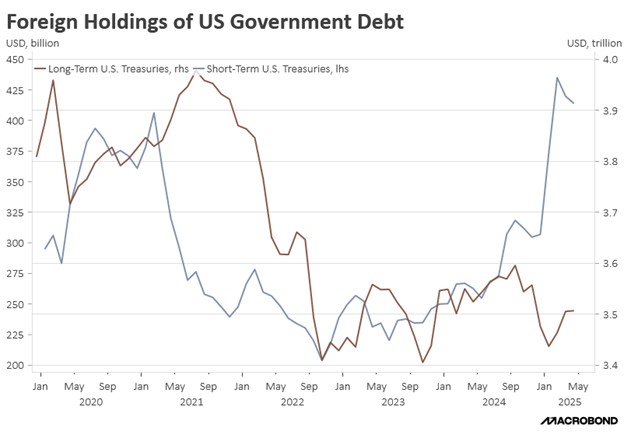
Tucked within the (ironically named) One Big, Beautiful Bill Act lies a provision that could dramatically reshape international capital flows. Section 899, colloquially termed the “revenge tax,” would empower the federal government to impose escalating taxes on the US passive income of individuals and corporations in countries with tax policies deemed discriminatory against American firms. This retaliatory tax, starting at 5% and potentially rising to 20%, represents a significant escalation in financial protectionism that could have far-reaching consequences for global markets.
Approximately $25.7 trillion in foreign-held US assets could potentially be affected. This includes $18.5 trillion in US equities (representing 20% of the market) and $7.2 trillion in Treasury securities (30% of the market). By taxing capital income going to foreigners, this provision risks weakening the demand for US Treasurys and could potentially trigger capital flight. The timing is particularly concerning as recent trade tensions have already sparked worries about the US dollar’s role as the global reserve currency. Substantial capital outflows could significantly increase the US’s borrowing costs and undermine the dollar’s global dominance.
The legislation specifically targets foreign policies that US lawmakers view as discriminatory, including the OECD’s two-pillar global tax framework (particularly its Undertaxed Profits Rule), various unilateral diverted profits taxes, and the EU’s Digital Services Tax. Washington considers these measures extraterritorial overreach that threatens US fiscal sovereignty while disproportionately harming American firms. The provision reflects populist concerns that foreign governments and supranational organizations are teaming up against US corporate interests in violation of established international norms.
Drawing inspiration from the reciprocal tariff measures unveiled in April, this legislation introduces a coercive framework that is designed to compel foreign governments to either rescind tax policies deemed discriminatory by the US or incur financial penalties. Republican lawmakers assert that certain OECD and eurozone tax initiatives fundamentally contravene core provisions of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), thereby creating direct conflicts with America’s established international tax framework. Specifically, the conflicts in question are with (1) Global Intangible Low-Taxes Income’s (GILTI) anti-profit-shifting rules, (2) Base Erosion and Anti-Abuse Tax’s (BEAT) anti-base erosion protections, and (3) Foreign-Derived Intangible Income’s (FDII) innovation incentives. Consequently, the revenge tax functions as both a punitive instrument and a defensive mechanism.
If Section 899 is included in the final legislation, the US technology sector may emerge as a significant beneficiary. With major US tech firms deriving 40-60% of their revenue from overseas, the threat of retaliatory taxes could pressure foreign governments to reduce their own levies on American companies. This potential upside, however, must be weighed against broader market concerns such as weaker demand for US-denominated assets, which could push up Treasury yields and reduce the attractiveness of US equities. In turn, those developments could slow the economy and weigh further on the dollar, although one benefit would likely be a narrowing of the US trade deficit.
Senate negotiators are working to modify the most controversial elements of Section 899, including clarifying the status of Treasury securities and potentially lowering initial tax rates. But the administration’s track record of aggressive policy implementation has left many investors skeptical of verbal assurances. As the bill progresses, global markets will be watching closely to see whether this represents a strategic recalibration of US economic policy or a potentially destabilizing shift in international financial relations. The ultimate impact may depend on how foreign governments and investors respond to what could be interpreted as a new era of financial nationalism.