by Patrick Fearon-Hernandez, CFA, and Thomas Wash
[Posted: 9:30 AM ET] | PDF
Our Comment today opens with news that Israel has agreed to strike only military targets in its expected attack on Iran, sparing oil and nuclear facilities. Global oil prices have therefore fallen sharply so far today. We next review several other international and US developments with the potential to affect the financial markets today, including heightened political tensions between India and Canada and a few words about the evolving military drone industry in the US.
Israel-Iran: According to a report in the Washington Post late yesterday, Israeli Prime Minister Netanyahu has told the US that his forces will only launch retaliatory strikes against Iranian military targets, rather than its oil or nuclear facilities. The report also said the Israeli attack would be calibrated to avoid the perception of political interference in the US elections.
- The suggestion that Tel Aviv is willing to exercise restraint after Iran’s latest missile attack has reduced the risk of a broader regional war that could cut global oil supplies.
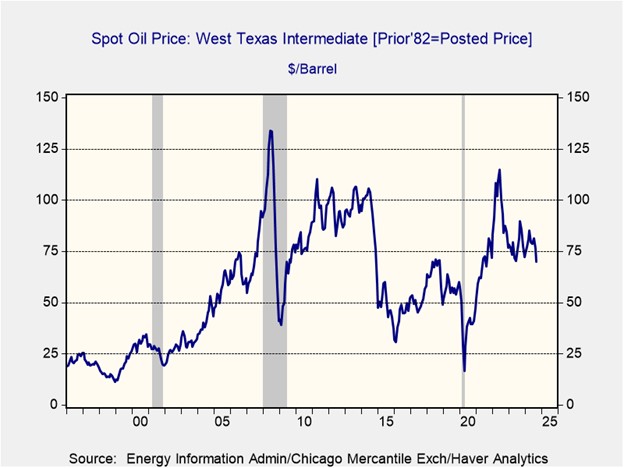
- As a result, global oil prices so far this morning have fallen sharply. Near Brent futures are currently down 3.9% to $74.43 per barrel, while WTI futures are trading down 4.2% to $70.75 per barrel.
China-Taiwan: Despite the welcome sign of cooling tensions in the Middle East, the Chinese military yesterday conducted large-scale exercises around Taiwan to retaliate for Taiwanese President Lai’s speech last week asserting the island’s sovereignty. Amid the drills, the Chinese military issued a statement saying, “This is a stern warning to the secession forces advocating ‘Taiwan independence.’”
- Beijing’s reaction to Lai’s speech shows the extent to which Taiwan’s moves to assert its sovereignty could provoke a Chinese military response.
- Of course, a strong Chinese military response could ultimately draw the US into a conflict in the Western Pacific Ocean.
Russia-Germany: In another reminder of today’s continuing geopolitical tensions, the head of Germany’s domestic intelligence agency yesterday told parliament that increasingly aggressive Russian agents had tried to sabotage a domestic airline flight earlier this year. The agents apparently got a parcel rigged to start a fire into the cargo hold of an airliner, but it burst into flames too early and didn’t cause a crash.
- The statement shows how Russian intelligence tactics are increasingly approaching the level of state-sponsored terrorism.
- The risk is that a successful attack could spark an international security crisis that would be highly disruptive to the global economy and financial markets.
Poland-European Union: Over the weekend, Polish Prime Minister Donald Tusk said his government will suspend immigrants’ right to asylum, making Poland the latest EU country to unilaterally curb migration. According to Tusk, the suspension is needed because Russia and Belarus are conspiring to send waves of migrants across the border to destabilize his country. The move is also in sync with widespread popular resistance to migration among EU citizens, but it will likely set up a clash with EU officials in Brussels.
Italy: The government of right-wing populist Prime Minister Meloni is reportedly in talks with the country’s banks to temporarily raise their taxes. The potential tax hikes would help cut Italy’s budget deficit down to the 3% of gross domestic product required by the EU. Of the 9 billion EUR ($9.82 billion) in tax hikes or spending cuts needed to meet the EU’s requirements in 2025, about one-third is expected to come from the nation’s banks. However, the liberal Forza Italia party, which is a member of the coalition government, is resisting further taxes on companies.
Canada-India: Ottawa yesterday declared six top Indian diplomats personae non grata and expelled them over allegations they had collected intelligence on Canadian Sikhs and targeted them for violence. In response, the Indian government expelled six Canadian diplomats. The expulsions are the latest results of India’s assassination of a Canadian Sikh separatist in British Columbia last year.
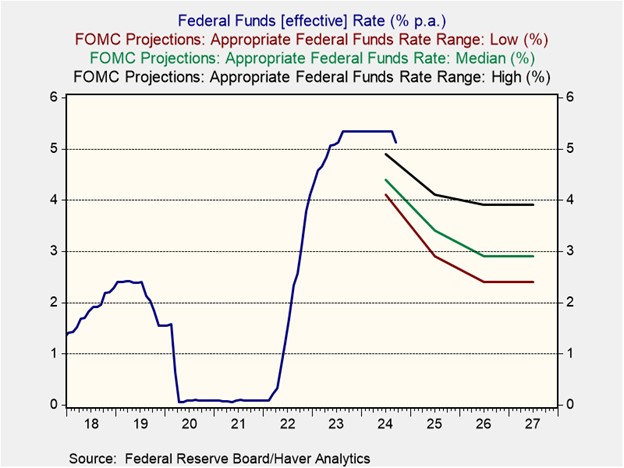
US Monetary Policy: Fed board member Christopher Waller yesterday said the monetary policymakers should exercise caution in cutting interest rates after last week’s report that September consumer price inflation was higher than expected and an earlier report that labor demand in September was more robust than anticipated. The statement confirms our view that the Fed will now cut rates much more gradually than its 50-basis-point cut last month.
US Defense Industry: Since the Russia-Ukraine war has shown that small, inexpensive drones are now key military systems for reconnaissance and attack, new reports suggest the US Army will soon need to buy thousands of drones per year just for training purposes. As it tries to figure out how to best use drones in war, the Army is now testing small drones and drone-operating units in three different brigades.
- Experience to date suggests each of the Army’s 59 active-duty and National Guard brigades would need at least 50 small drones, and perhaps more than 100, for training. That implies a total fleet of 3,000 to 6,000 drones. Army officials assume about 25% of those drones would be lost each year, implying annual replacement buys of 750 to 1,500. Those totals don’t include the Army’s purchases of bigger, heavier drones or purchases by the Navy, Marines, and Air Force.
- Of course, the Russia-Ukraine war shows that the military would need to buy multiples of those figures to prepare for a potential war. It would also need to invest in the surge capacity to produce enormous numbers of drones of various types. For comparison, Ukrainian President Zelensky recently said his country’s defense industry has now developed the capacity to produce 4 million drones per year.
- We continue to believe worsening geopolitical tensions will spur increased defense budgets around the world. However, purchases of big, heavy, expensive systems such as fighter jets and tanks may be cut to fund purchases of relatively inexpensive drones. The defense budgets of the US and its allies may therefore be restructured over time.
- We still expect US spending on big, expensive, “exquisite” military systems will rise, but the growth rate will likely pale when compared with the spending hikes related to drones and other new technologies. The prime defense contractors that build the traditional systems, therefore, may not grow as fast as small defense start-ups or small companies producing high-tech products with dual civilian and military uses. As those firms eventually have their initial public offering of stock, they may be interesting investment opportunities.
US Nuclear Energy Industry: Late yesterday, Google said it has struck a deal to back the construction of seven small, modular nuclear reactors by nuclear energy start-up Kairos Power. Under the deal, Google has committed to buy some 500 megawatts of electricity from the reactors as they come on-line between 2030 and 2035. The deal is the latest example of firms signing up for nuclear energy to power their artificial-intelligence efforts without boosting their greenhouse gas emissions.
US Property Insurance Industry: Initial estimates show last week’s Hurricane Milton will lead to about $36 billion in private-sector insurance payouts, versus new estimates that Hurricane Helene will result in about $6 billion in payouts. The total estimated payouts for the two storms are significantly lower than initially feared. Reflecting the lower-than-feared payouts, major reinsurance stocks have now generally regained their prices from before the storms hit.
US Medicare Insurance Industry: The enrollment period for 2025 Medicare insurance plans opens today and will run through December 7. Because of changes by federal authorities and insurance companies, an estimated 1.5 million seniors will have their Medicare Advantage plan eliminated next year, while 3.5 million will lose their Plan D drug coverage. Many others are expected to see benefit reductions and/or deductible increases in their plans.