by Patrick Fearon-Hernandez, CFA, and Thomas Wash
[Posted: 9:30 AM ET] | PDF
Good morning! Markets are in a risk-on mode today after yesterday’s robust inflation data. In sports news, Real Madrid kicked off their 2024/25 season with a triumphant UEFA Super Cup victory, and now set their sights on defending both their Champions League and La Liga titles. Today’s Comment examines the Fed’s challenges in taming lingering inflation, the mounting regulatory pressures on tech companies, and the evolving Chinese economic landscape. As always, we conclude with a comprehensive overview of domestic and international news.
Inflation Pressures Ease: The July CPI report fueled optimism among investors that the Federal Reserve will lower interest rates in September, but questions persist regarding the size of the cut.
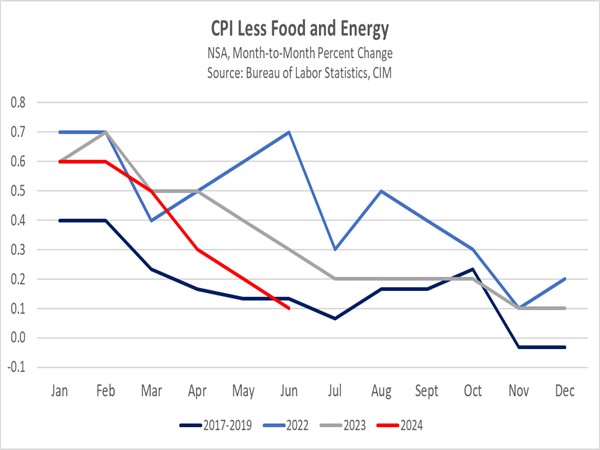
- Inflation eased to a three-year low last month, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. The headline Consumer Price Index (CPI) decelerated from 3.0% to 2.9%, while the core CPI, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, softened to 3.2% from 3.3%. These figures aligned with market forecasts and increased expectations for a potential interest rate cut in September. However, despite the positive report, market expectations for a rate cut have moderated, with odds of a 25 basis-point reduction now favored over a 50 basis-point cut, according to the CME FedWatch Tool.
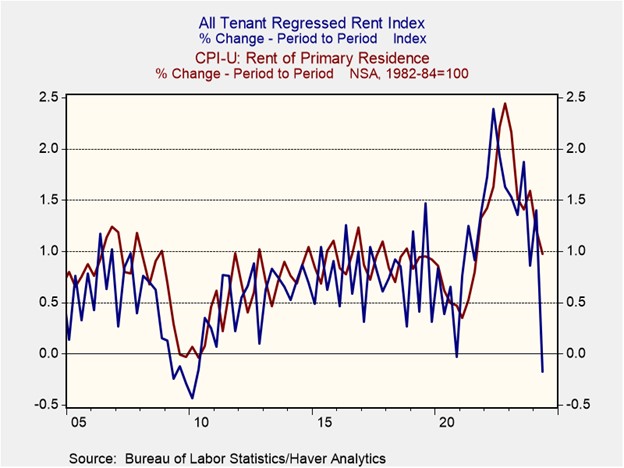
- A primary driver of the shift in market expectations was the unexpected resurgence of housing inflation. Shelter costs accelerated from a month-over-month increase of 0.2% to 0.4%, challenging the notion that housing inflation, especially rental prices, had begun to cool. Fed officials have long anticipated the incorporation of market rent data into CPI figures, but technical issues, such as the timing of pandemic-related eviction moratorium expirations, have complicated the pass-through effects.
- With one CPI and one PCE price report to go before the next Fed meeting, the central bank is likely to lean toward a rate cut if inflation continues on its current trajectory. However, the size of any potential rate cut will hinge primarily on the upcoming jobs report. Several Fed officials have signaled that an unexpected increase in unemployment could pave the way for Fed action. Given the Fed’s most recent projections with the most pessimistic scenario forecasting a 4.4% unemployment rate by year-end, any reading above this level would likely necessitate a more aggressive policy response.
Trust Busting?: Tech giants are increasingly resembling the monopolistic power of Standard Oil as governments intensify scrutiny of their market dominance.
- A federal court ruling has found Google guilty of illegally monopolizing the search engine and search text ad markets. As a result, the Department of Justice (DOJ) is considering breaking up the tech giant. The court determined that Google’s $26 billion payments to make its search engine the default on smartphones and web browsers effectively blocked competition. While Google plans to appeal the decision, the judge has ordered both parties to explore remedies to restore competition. Potential consequences of a breakup include the divestiture of Alphabet’s Android, AdWords, and Chrome.
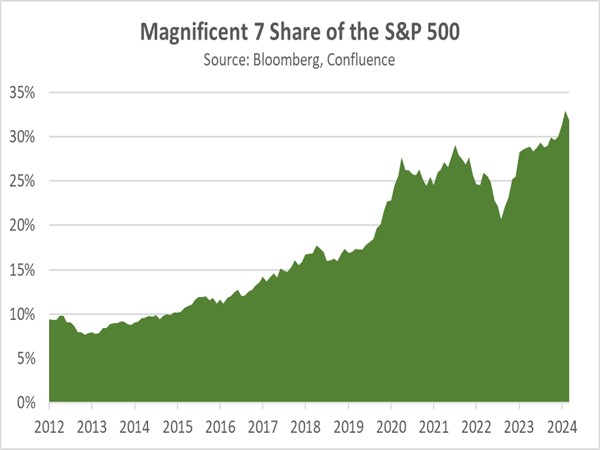
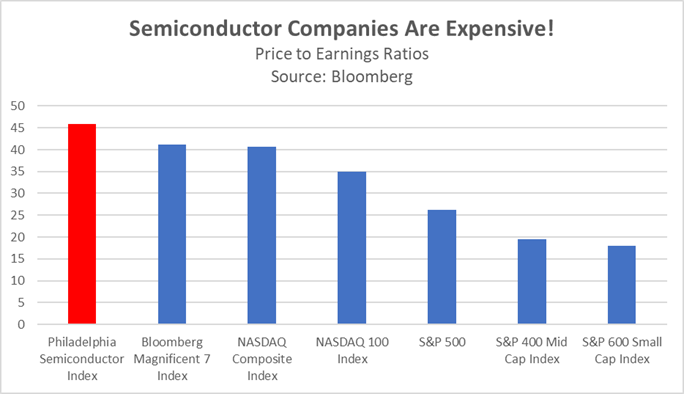
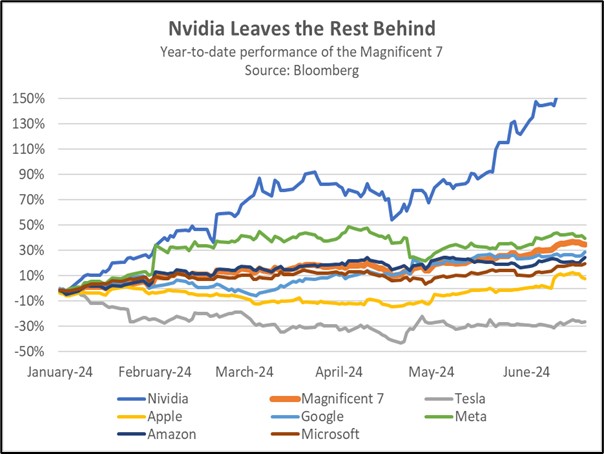
- The recent ruling against Google is part of a broader global effort to curb the power of tech giants. The DOJ is also targeting Apple for alleged anti-competitive behavior in the smartphone market. Simultaneously, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) is challenging Amazon’s practices that restrict sellers from offering lower prices on other platforms. Overseas, European regulators have accused Meta of violating the bloc’s Digital Markets Act with its pay or consent advertising model. The decision to go after major tech companies has occurred as the equity market has become more concentrated.
- It’s important to note that despite regulatory pressures, tech companies have yet to be forced to break up their businesses. In fact, the last major company breakup occurred in the 1980s with AT&T, but a similar attempt to dismantle Microsoft in 2001 was unsuccessful. Despite these challenges, tech giants may be forced to relinquish some of their market dominance as they look to appease regulators. The increased competition and diminished pricing power of these firms will erode their profitability, leading to a broader market concentration over the next decade.
China’s Economic Woes Continue: China’s economic slowdown, exacerbated by trade disputes and debt, casts a long shadow over the global economy.
- New economic data has led to concerns about the current state of the Chinese economy. China’s industrial output slowed to its weakest pace in four months in July, expanding at a rate below expectations. Meanwhile, the unemployment rate edged up from 5.0% to 5.2%. The real estate market remains a significant concern for policymakers, with the home price index falling even deeper into contraction territory. Home prices dropped 4.9% year-over-year in July, compared to a decrease of 4.5% in the previous month.
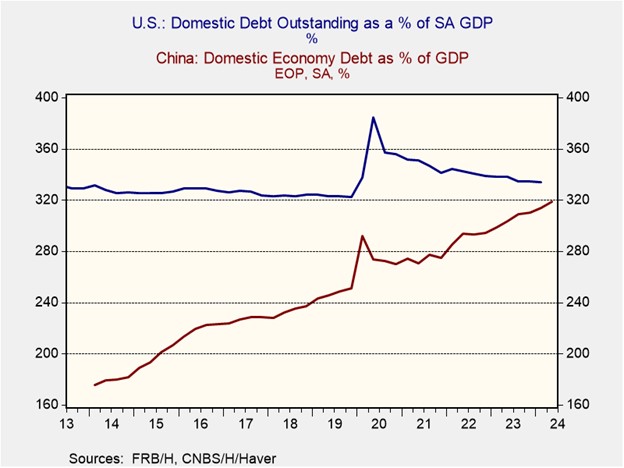
- Weak economic indicators are likely to increase pressure on Beijing to bolster growth. The government has been cautious about deploying significant fiscal stimulus due to mounting debt concerns. Unlike its major economic peers, which have sought to stabilize their debt levels, China has continued to accumulate debt. Its total debt-to-GDP ratio, comprising household, corporate, and government liabilities, has exceeded 300% and is on course to outstrip the US’s ratio within the next few quarters. This rapid debt accumulation has intensified fears of a debt trap as China strives to maintain its growth trajectory.
- While elevated debt levels pose risks to economic expansion, a prudent approach to debt management can strengthen investor confidence. By carefully calibrating stimulus measures and avoiding fiscal excess, the government can sustain growth while gradually addressing its debt burden. Although this strategy may not swiftly resolve the debt challenge, it can mitigate the risk of a severe economic downturn. Consequently, while we don’t expect growth to be strong, we still see a lot of investable opportunities in the region.
In Other News: Google reports that members of the Trump, Biden, and Harris teams were all targets of a phishing campaign from Iran. The hack highlights the growing prevalence of cyberwarfare. Vice presidential candidate Tim Walz agreed to debate JD Vance on October 1. The showdown will likely be used to win over swing voters in the Rust Belt.